New highlights added 2023-11-29
n (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-03-11
Hyper Log Log. What are they based on
Some databases have implemented approximate versions of the functions that are faster to compute and generally return high-quality results if absolute precision is not required (View Highlight)
Whenever we make a query, we must perform sanity checks
Profiling: Data Quality (View Highlight)
This is the easiest way
As an alternative to a subquery, you can use a HAVING clause and keep everything in a single main query. Since it is evaluated after the aggregation and GROUP BY, HAVING (View Highlight)
But please check why so we having duplicates
One way to remove duplicates is to use the keyword DISTINCT (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-03-10
data munging, data wrangling, and data prep. (“Mung” is an acronym for Mash Until No Good, which I have certainly done on occasion.) (View Highlight)
If we can, we better do this step on BI
This can’t be solved with a simple query; it requires an intermediate aggregation step, which can be accomplished with a subquery. (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-03-13
w (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-03-15
e (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-03-19
b.user_id (View Highlight)
a.user_id (View Highlight)
Consider including time boxes, to only include users who complete an action within a specific time frame, if users can reenter the funnel after a lengthy absence (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-05-21
t (View Highlight)
t (View Highlight)
Ver y recordar el caso de null.
Cleaning Data with CASE Transformations (View Highlight)
A concept related to but slightly different from nulls is empty string (View Highlight)
For example, we might expect that each customer in the transactions table also has a record in the customer table. To check this, query the tables using a LEFT JOIN and add a WHERE condition to find the customers that do not exist in the second table: SELECT distinct a.customer_id FROM transactions a LEFT JOIN customers b on a.customer_id = b.customer_id WHERE b.customer_id is null (View Highlight)
Explain the case of BI tools (particularly Hex)
For Which Output: BI, Visualization, Statistics, ML (View Highlight)
To avoid this we need to use Jinja or Python
Although this syntax is more compact than the CASE construction we saw earlier, the desired columns still need to be specified. (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2024-06-19
Generally, the output for modeling will fol‐ low the notion of “tidy data” proposed by Hadley Wickham.2 (View Highlight)
New highlights added 2025-04-04
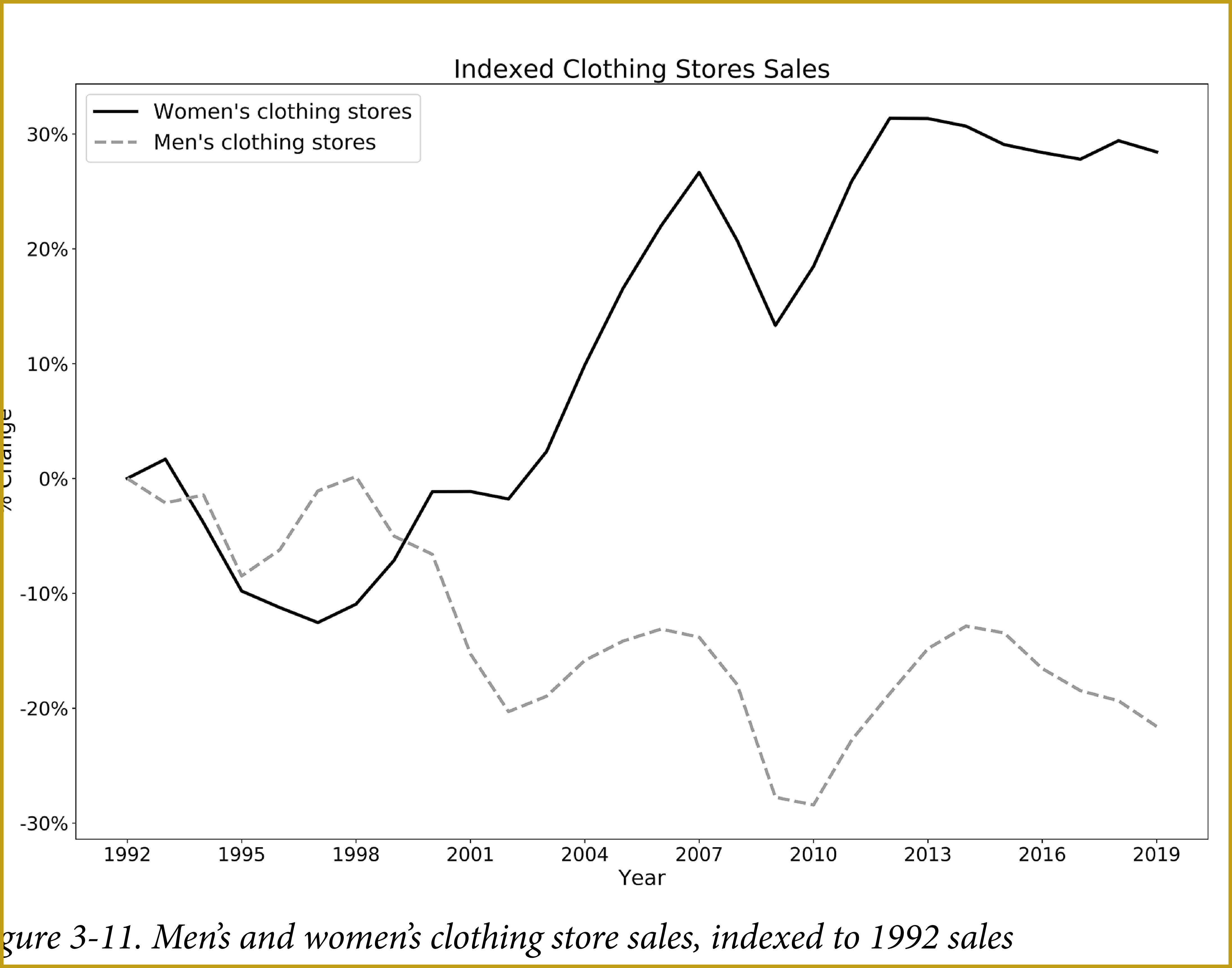
Indexing to See Percent Change over Time (View Highlight)
retention in the starting period is always 100%. Over time, retention based on counts generally declines and can never exceed 100%, whereas money- or action-based retention, while often declining, can increase and be greater than 100% in a time period. (View Highlight)
 (
(